Information Cybersecurity
NETWALK promises to deliver against its strategic aims by reducing the risk of significant security incidents and data breaches including unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, inspection, recording or destruction of information.

Infrastructure Security
As organizations seek to leverage AI and big data analytics to drive efficiencies in their operations through “smart networks,” IT and OT networks are converging. In a word, these complex industrial control systems are now connected to the internet, making them vulnerable to hacking. Because many of these industrial control systems were not designed with cybersecurity in mind, it’s not surprising they draw hackers’ attention when these older systems are connected to the internet. Throw in the exponential growth of the internet of things (IoT), and it’s clear the threat vector faced by critical infrastructure operators has grown substantially.
Endpoint Security
Increasingly, enterprises and their employees are incorporating practices to make access to data more fluid. The increase in BYOD (bring your own device) policies, in addition to threats targeting mobile device access and networks, create multiple endpoint vulnerabilities. In addition, employees working from home or connecting to Wi-Fi networks to work on-the-go means that the enterprise network security perimeter is more porous than ever. In the past, most security breaches came in through the network. Today, however, threats are increasingly coming in through endpoints, which means centralized network protection does not go far enough. Shifting security perimeters that lack clear definition require new layers of security through endpoint protection. Security must maintain greater control over access points to prevent the vulnerabilities that can arise through the use of remote devices. Read More

Cloud Security
Cloud security, also known as cloud computing security, consists of a set of policies, controls, procedures and technologies that work together to protect cloud-based systems, data and infrastructure. These security measures are configured to protect data, support regulatory compliance and protect customers’ privacy as well as setting authentication rules for individual users and devices. From authenticating access to filtering traffic, cloud security can be configured to the exact needs of the business. And because these rules can be configured and managed in one place, administration overheads are reduced, and IT teams empowered to focus on other areas of the business.
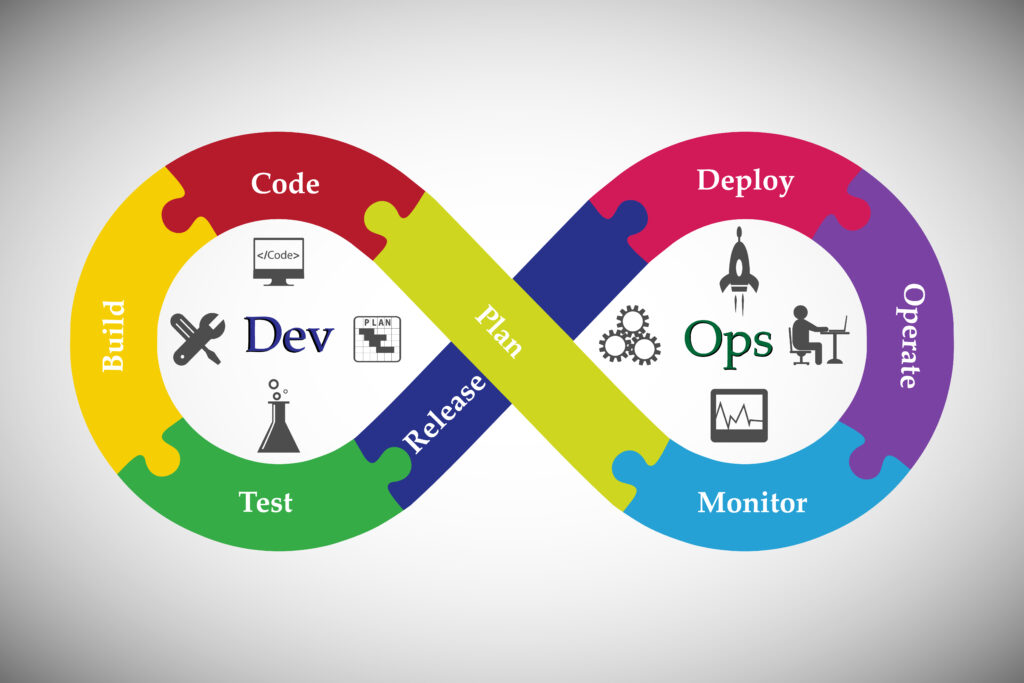
DevOps
DevOps is a set of practices that automates the processes between software development and IT teams, in order that they can build, test, and release software faster and more reliably. The concept of DevOps is founded on building a culture of collaboration between teams that historically functioned in relative siloes. The promised benefits include increased trust, faster software releases, ability to solve critical issues quickly, and better manage unplanned work.
It’s a firm handshake between development and operations that emphasizes a shift in mindset, better collaboration, and tighter integration. It unites agile, continuous delivery, automation, and much more, to help development and operations teams be more efficient, innovate faster, and deliver higher value to businesses and customers.

Compliance
Compliance was meant to be a floor, but it has become a ceiling. Industry standard certifications and compliance frameworks (for example, HIPPA, PCI, ISO) are the bare minimum and intended to be generic. A framework can’t account for the nuances of your company operations and environment. These audits only look at a snapshot in time, not the ongoing state of your security. Your company could pass an audit, but a day later a vulnerability could be left unaddressed and your security compromised. We’ll say it again: Compliance is not security. The most cyber-resilient organizations are those that treat compliance as a baseline.
Web Application Security
To ensure that a web application is secure you have to identify all security issues and vulnerabilities within the web application itself before a malicious hacker identifies and exploits them. That is why it is very important that the web application vulnerabilities detection process is done throughout all of the SDLC stages, rather than once the web application is live.
There are several different ways to detect vulnerabilities in web applications. You can scan the web application with a black box scanner, do a manual source code audit, use an automated white box scanner to identify coding problems, or do a manual security audit and penetration test.